Future value is crucial to making informed investment decisions
Written byCFI Team
Reviewed byJeff Schmidt
What is Future Value?
There are many calculations a financial analyst must master. One of these calculations is the future value (FV) calculation. Understanding future value is crucial for financial planning and investment decision-making.
Fundamentally, future value is how much an investment made today will be worth at some point in the future. Therefore, future value is critical in making informed decisions about investments or even savings. In this article, we will further discuss future value, how to utilize the future value formula, and how to apply it in different financial scenarios.
Key Highlights
- Future value is how much an investment made today will be worth at some point in the future, which makes it crucial in making informed decisions about investments.
- The future value formula is FV=PV*(1+r)^n, where PV is the present value of the investment, r is the annual interest rate, and n is the number of years the money is invested.
- The Excel function FV can be used when there is a constant interest rate. This function can also take into account additional investments beyond the initial investment/present value.
The Future Value Formula
The future value is simply the expected future value of an investment made today. The future value formula assumes the investment will grow at some rate over a specific time period.
For example, assume we have $1,000 today and we invest it at 5% for one year. In one year, we will have $1,050.00. In this simple example, the future value is calculated as the present value*(1+the interest rate), or 1000*(1.05).
If we made the same investment for two years, the future value would be $1,102.50. In this case, the initial investment compounded over two years, so the formula is 1000*(1+5%)^2. Compound interest benefits investors as interest is earned on both the original investment of $1,000 and the first year’s interest of $50.
Breaking this down further the original investment grows to $1,050 in the second year. However, the second year’s interest is $50 plus interest on the first year’s interest of $50. The interest on the first year’s interest is $2.50 ($50*5%). Adding all of this up is the same $1,102.50 mentioned earlier.
Of course, we don’t have to calculate interest on interest for every year… this could get quite cumbersome if there are many years! Instead, we can rely on the future value formula:
FV = PV*(1+r)^n
Where:
- FV is the future value of the investment, including growth/interest.
- PV is the present value of the investment.
- r is the annual interest rate.
- n is the number of years the money is invested.
This formula can be used for calculating the future value of an investment when the interest is compounded annually. The formula above incorporates the principle of compounding by including the exponent n.
Of course, future value can be extended to more complex situations, such as different compounding periods (monthly, quarterly, etc.), continuous compounding, or applied to a series of cash flows.
Compound Interest: An Investor’s Best Friend
Legendary investor Warren Buffet called compound interest an investor’s best friend. Even Albert Einstein said: “Compound interest is the eighth wonder of the world. He who understands it, earns it … he who doesn’t … pays it.”
Compound interest is the process where an investment earns interest not only on the principal but also on the interest that accumulates over previous periods.
Compounding plays an absolutely critical role in determining the future value of an investment. In our earlier examples we assumed compounding was on an annual basis. However, this is not always the case. Different compounding periods, like quarterly or monthly, can significantly affect the investment’s future value. As a rule, the more frequently interest is compounded, the greater the future value will be.
The basic future value formula is instrumental for calculating the growth of a single sum. However, for additional investments (or even withdrawals), the formula needs to be adjusted to handle these cash flows.
Using the FV Function in Excel
Excel has a useful function known as FV, which calculates the future value of an investment. This function can be used when there is a constant interest rate. It can also take into account additional investments beyond the initial investment/present value. However, the additional investments must be constant.
Formula Syntax
=FV(rate,nper,pmt,[pv],[type])
This function uses the following arguments:
- Rate (required argument): This is the interest rate for each period.
- Nper (required argument): The total number of payment periods.
- Pmt (optional argument): This specifies the payment per period. If we omit this argument, we need to provide the PV argument.
- PV (optional argument): This specifies the present value (PV) of the investment/loan. The PV argument, if omitted, defaults to zero. If we omit the argument, we need to provide the Pmt argument.
- Type (optional argument): This defines whether payments are made at the start or end of the year. The argument can either be 0 (payment is made at the end of the period) or 1 (the payment is made at the start of the period). A payment at the end of a period is sometimes known as an ordinary annuity, while a payment at the beginning of the period is sometimes known as an annuity due. This is important because a payment made at the beginning of a period will have the opportunity to earn interest in that period, whereas a payment made at the end of the period will not.
However, we must make sure the units of rate and nper are consistent. If we make monthly payments on a five-year loan at an annual interest rate of 10%, we need to use 10%/12 for rate and 5*12 for nper. If we make annual payments on the same loan, then we would use 10% for rate and 5 for nper.
Using our earlier example of an initial investment amount of $1,000, a 5% interest rate and a two-year period (assuming annual compounding), the FV formula returns the same $1,102.50 calculated above.
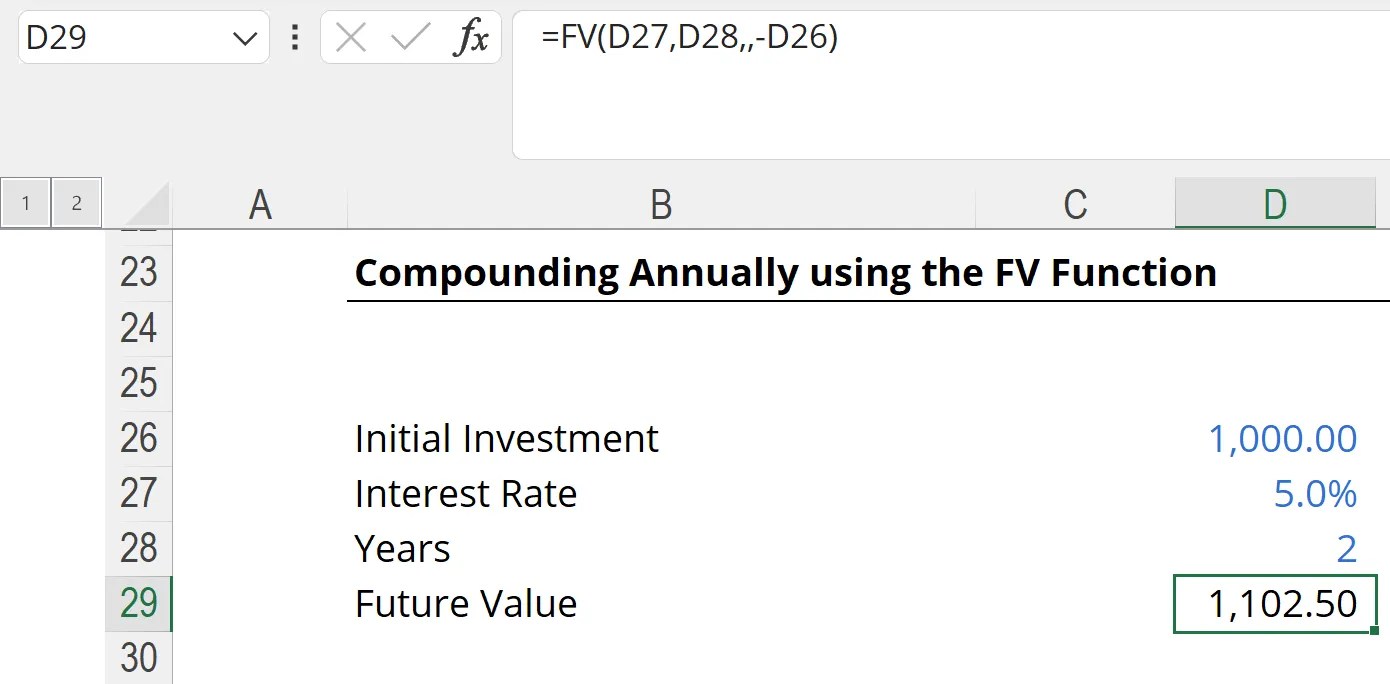
Note that we enter the initial investment (cell D26) as a negative number, otherwise the FV function will return a negative $1,102.50. Since we included the initial investment/present value, we did not include a payment, hence why there is nothing in the function between D28 and -D26.

In this case, we included an additional payment of $100 made in each of the two years. By omitting the optional argument “Type,” the FV function assumes the payments are made at the end of the year. Again, we made the payment a negative number, as well as the present value.
If we want to vary the compounding frequency, we must modify both the rate, nper, and pmt arguments in the FV function.

In the above screenshot, we divided the interest rate by 12 to obtain a monthly interest rate. Additionally, we multiplied the number of years by 12 to reflect that there are 24 compounding periods over two years.
Finally, in our earlier example, we assumed the $100 additional payment was an annual number; to convert it to a monthly number, we divided the payment by 12. You can see the greater compounding frequency increases the future value from $1,307.50 in our previous example to $1,314.82. This is the beauty of compound interest.
The weakness of the FV function is that we assume the interest rate is a constant rate, as are the additional payments. If this is not the case, then we would need to create a more in-depth spreadsheet to properly capture everything.
Calculating the Future Value of a Growing Payment
If the payment is not constant and is instead growing (or even getting smaller), then the FV function can’t really handle what we need. In this case, it’s better to actually project out the payments and calculate the future value manually, as shown below (payments are assumed to occur at the end of the period).
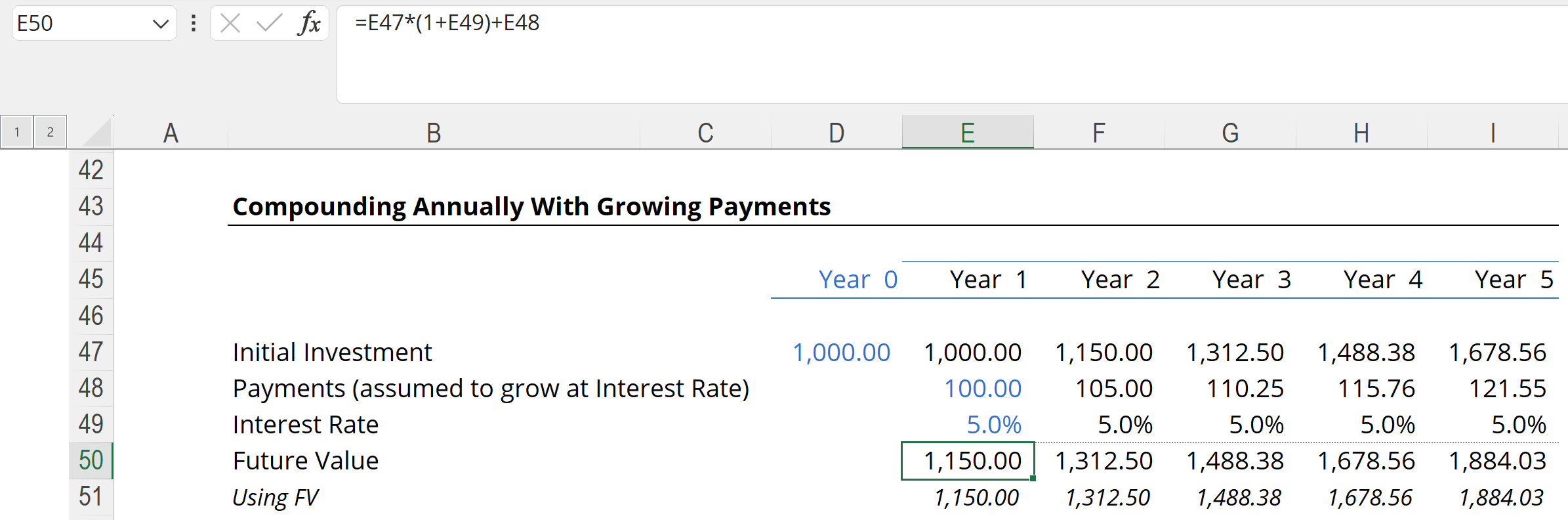
Factoring in Inflation and Taxes
Future value calculations can also be adjusted to factor in things like inflation and taxes. Both of these erode the purchasing power of the future value. Incorporating these elements provides a more realistic estimate of the investment’s future value. These added complications may be better included by projecting out the investment manually instead of using Excel’s FV function.
Download the Free Template
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now!
Continuous Compounding
The concept of continuous compounding is used in some financial calculations; however, there is no actual investment (or debt instrument) that continuously compounds. Instead, in everyday banking and most personal finance products, interest is compounded on a period basis like monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Even though it is essentially mostly theoretical, continuous compounding is often used when pricing and valuing derivatives, foreign exchange, and futures contracts. In this case, continuous compounding provides a useful approximation when analyzing these complex products.
Continuous compounding represents the mathematical limit that compounded interest can reach. It assumes interest is calculated and reinvested over an infinite number of periods.
The formula for continuously compounded interest is derived from the general formula and is as follows:
FV=PVe^(r*n)
Where:
- FV is the future value, including interest earned.
- PV is the present value/initial investment.
- e is the base of the natural logarithm, approximately equal to 2.718282.
- r is the annual interest rate.
- n is the number of years.

As shown in the screenshot above, Excel’s EXP function can help when calculating the future value of a continuously compounded investment.
As mentioned earlier, continuous compounding is mostly theoretical and really only used in pricing models of options and other derivatives. For example, continuous compounding is used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which assumes a continuously compounding risk-free rate.
Future Value vs. Present Value
Future value is closely linked to present value. Future value is focused on determining the future value of an amount today, and present value is trying to determine today’s value of an amount in the future.
Both future value and present value use similar variables like interest rate and number of periods. You can work backward to find present value and forward to find future value. Using our simple example above, if we have $1,050 in one year, we can calculate the present value today using the following formula:
PV = FV/(1+r)^n
Where:
- PV is the present value of the amount.
- FV is the future value of the amount.
- r is the annual interest rate.
- n is the number of years the money is invested.
Assuming a 5% interest rate, the present value is $1,000 (1,050/(1+5%)^1).
Seek Professional Financial Advice for Complex Situations
While the future value formula provides a way to estimate an investment’s potential future worth, financial planning will often involve numerous complexities that limit the use of the basic future value calculation. Therefore, it’s important to seek professional financial advice when dealing with different financial scenarios, tax implications, and investment strategies.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Future Value. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- Continuous Compounding
- DCF Valuation Modeling Course
- Black Scholes Calculator
- Time Value of Money
- See all valuation resources
- See all wealth management resources