Creating an Express.js application involves several steps that guide you through setting up a basic server to handle complex routes and middleware. Express.js is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. Here’s a comprehensive guide to get you started with your Express.js application.
Table of Content
- Steps to Create an Express.js Application
- Setting GET request route on the root URL
- Setting up one more get request route on the ‘/hello’ path.
- Setting route to be accessed by users to send data with post requests.
Steps to Create an Express.js Application
Step 1: Write this command to create a NodeJS application in your terminal because our express server will work inside the node application.
npm initThis will ask you for a few configurations about your project you can fill them in accordingly, also you can change them later from the package.json file.
Note: Use ‘npm init -y’ for default initialization

Step 2: Install the necessary dependencies for our application. In this, we will install express.js dependency.
npm install expressSomething like this will be shown on successful installation.

Step 3: Create an app.js (or server.js) file. This will serve as the main entry point for your application.
Project Structure:

The updated dependencies inpackage.jsonfile will look like:
"dependencies": { "express": "^4.19.2", "mongoose": "^8.4.0" }Approach
- Use require(‘express’) to import the Express module.
- Call express() to create an Express application instance.
- Define the port for the application, typically 3000.
- Set up a basic GET route with app.get(‘/’, (req, res) => res.send(‘Hello World!’)).
- Use app.listen method to listen to your desired PORT and to start the server.
Example: Implementation to setup the express application.
const express = require('express');const app = express();const PORT = 3000;app.listen(PORT, (error) =>{ if(!error) console.log("Server is Successfully Running, and App is listening on port "+ PORT) else console.log("Error occurred, server can't start", error); });
Step to Run Application:Run the application using the following command from the root directory of the project
node app.jsOutput: You will see something like this on the terminal.

Now with all of this, we have created and run the server successfully, if your server is not starting then there may be some error, try to analyze and read that error and resolve it accordingly.
Finally, after a successful run if you try to open the URL (localhost:3000) on the browser it will show you cannot GET / because we have not configured any route on this application yet.
Step 4: Now we will set all the routes for our application.
Routes are the endpoints of the server, which are configured on our backend server and whenever someone tries to access those endpoints they respond accordingly to their definition at the backend. If you’re a beginner you can consider route as a function that gets called when someone requests the special path associated with that function and return the expected value as a response. We can create routes for HTTP methods like get, post, put, and so on.
Syntax:
The basic syntax of these types of routes looks like this, the given function will execute when the path and the request method resemble.
app.anyMethod(path, function)Setting GET request route on the root URL
- Use app.get() to configure the route with the path ‘/’ and a callback function.
- The callback function receives req (request) and res (response) objects provided by Express.
- req is the incoming request object containing client data, and res is the response object used to send data back to the client.
- Use res.status() to set the HTTP status code before sending the response.
- Use res.send() to send the response back to the client. You can send a string, object, array, or buffer. Other response methods include res.json() for JSON objects and res.sendFile() files.
Example: Implementation to set up a basic request route on the root URL.
//app.jsconst express = require('express');const app = express();const PORT = 3000;app.get('/', (req, res)=>{ res.status(200); res.send("Welcome to root URL of Server");});app.listen(PORT, (error) =>{ if(!error) console.log("Server is Successfully Running, and App is listening on port "+ PORT) else console.log("Error occurred, server can't start", error); });
Step to run the application: Save this code, restart the server, and open the localhost on the given port. When a client requests with the appropriate method on the specified path ex: GET request on ‘/’ path, our function returns the response as plain text If we open the network section in Chrome developers tools (press Ctrl+Shift+I to open) we will see the response returned by the localhost along with all information.
Output:

Setting up one more get request route on the ‘/hello’ path.
- Most of the things are the same as in the previous example.
- The set() function is used to set the HTTP header’s content type as HTML. When the browser receives this response it will be interpreted as HTML instead of plain text.
- Also in this example, we are not explicitly setting status, it is now concatenated with the statement of sending the response. This is another way to send status along with a response.
Example: Implementation to setup the one more route.
//app.jsconst express = require('express');const app = express();const PORT = 3000;app.get('/hello', (req, res)=>{ res.set('Content-Type', 'text/html'); res.status(200).send("<h1>Hello GFG Learner!</h1>");});app.listen(PORT, (error) =>{ if(!error) console.log("Server is Successfully Running, and App is listening on port "+ PORT) else console.log("Error occurred, server can't start", error); });
Step to run the application: Save this code, restart the server, and open the localhost on the given port. Now access the ‘/hello’ route from the browser, The h1 text inside HTML will be shown as a response.
Output:
Step 5: Now we will see how to send data to the server.
Sometimes we have to send our data to the server for processing, for example when you try to log in on Facebook you send a password and email to the server, Here we will see how to receive data from the user request. We can send data with the request object on the specified path with appropriate HTTP methods. Till now we were using the browser to interact with the server, but in this step, any tool or frontend form is must be needed to send data because the browser search bar can only send get requests to receive resources from the server.
Setting route to be accessed by users to send data with post requests.
- Before creating a route for receiving data, we are using an inbuilt middleware, Middleware is such a broad and more advanced topic so we are not going to discuss it here, just to understand a little bit you can think of this as a piece of code that gets executed between the request-response cycles.
- The express.json() middleware is used to parse the incoming request object as a JSON object. The app. use() is the syntax to use any middleware.
- After that, we have created a route on path ‘/’ for post request.
- const {name}, which is the syntax in ES6 to extract the given property/es from the object. Here we are extracting the name property that was sent by the user with this request object.
- After that, we are simply sending a response to indicate that we have successfully received data. If this `${} ` is looking weird to you then let me tell you that it is the syntax in ES6 to generate strings with javascript expression in ES6. We can inject any javascript expression inside ${}.
Example: Implementation to Setup route to be accessed by users to send data with post requests.
// app.jsconst express = require('express');const app = express();const PORT = 3000;app.use(express.json());app.post('/', (req, res)=>{ const {name} = req.body; res.send(`Welcome ${name}`);})app.listen(PORT, (error) =>{ if(!error) console.log("Server is Successfully Running, and App is listening on port "+ PORT) else console.log("Error occurred, server can't start", error); });
Step to run the application: We are Accessing the route with Postman. It is a tool to test APIs, we can use any other things like Axios, fetch, or any other thing from the frontend or cURL from the terminal, but that will make you divert from the topic, just keep in mind that our express server only demands a path with request object it doesn’t matter from where it is coming. We have sent the data as a JSON object with the request body and express is sending a response back to us along with the data. It indicates that our goal to send data to the server succeeded.
Output:

Step 6: Sending Files from Server
Step 7: Now we will see how to send files from the server.
Several times we need to transfer the resources from the server as per user request, there are majorly two methods to send files one is sending static files using middleware and the other one is sending a single file on a route.
This is our folder structure and we want to serve the files from the Static Files directory as static files, and the image.jpg on a separate route.

Example 1: Serving entire directory using middleware
In Express, we use the middleware express.static() function, which takes two arguments. The first argument is the absolute root path of the directory containing the files we want to serve. We can easily serve static files by using app.use() and providing the express.static() middleware.
Syntax:
app.use(path, express.static(root, [options]));- First of all, we are importing an inbuilt module `path`, because later we are going to use one of the functions provided by this module.
- We are simply mounting a middleware at the ‘/static’ route.
- The static() middleware requires an absolute path so we use the path module’s join method.
- The join() method takes two parameters and joins them as a path, in NodeJS we have a global attribute __dirname which contains the path of the directory in which the current file exists.
- We are providing that joined path to middleware so that it can start serving the files inside that directory on the given path.
Example: Implementation to show the use of middleware in Express.
// app.jsconst express = require('express');const app = express();const PORT = 3000;const path = require('path')app.use('/static', express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'Static Files')))app.listen(PORT, (error) =>{ if(!error) console.log("Server is Successfully Running, and App is listening on port "+ PORT) else console.log("Error occurred, server can't start", error); });
Step to run the application: This will be the returned response when we request some static file from the directory that we are serving as static. Here you can see we have received an HTML file as a response for ‘/static/random.html’. The same things happen when we request for ‘/static/1.jpg’.
Output:
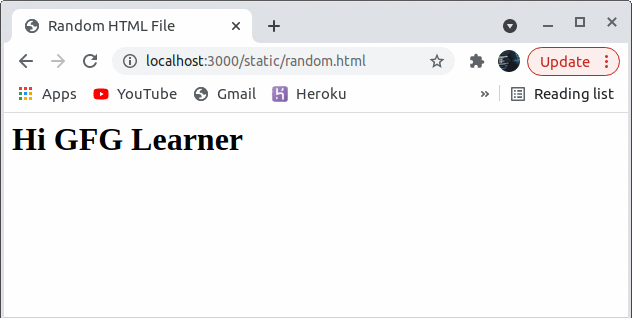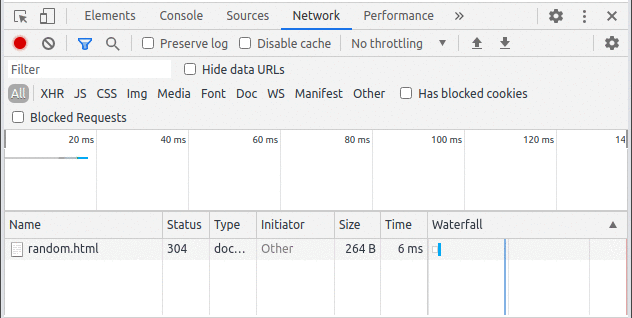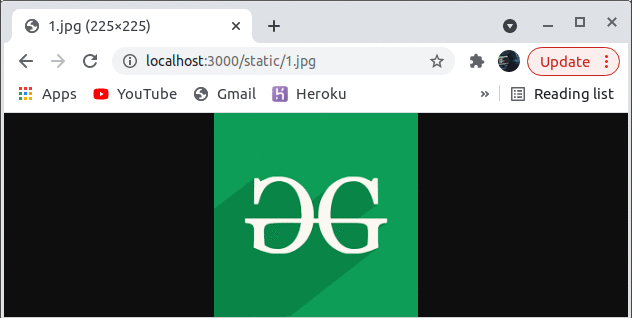
Example 2: Sending a single file on a route with the sendFile() function.
This function accepts an absolute URL of the file and whenever the route path is being accessed the server provides the file as an HTTP response. This process can be thought of as a single endpoint of the express.static(). It can be useful when we have to do some kind of processing before sending the file.
Syntax:
res.sendFile(fileUrl)- We are creating a get request route on the ‘/file’ path
- After that we create the absolute path by joining the path of the current __dirname and the name of the file we want to send and then passing it to sendFile().
- The route sends the image.jpg file to the user as an HTTP response.
Example: Implementation to show Sending a single file on a route with the sendFile() function.
// app.jsconst express = require('express');const path = require('path');const app = express();const PORT = 3000;app.get('/file', (req, res)=>{ res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname,'image.jpg'));});app.listen(PORT, (error) =>{ if(!error) console.log("Server is Successfully Running, and App is listening on port "+ PORT) else console.log("Error occurred, server can't start", error); });
Output: After running the server, When we request the route ‘/file’ the server sends the image.jpg file as a response.

Previous Article
Introduction to Express
Next Article
Print hello world using Express JS
