by Anupama Sapkota
Serial dilution, as the name suggests, is a series of sequential dilutions that are performed to convert a dense solution into a more usable concentration.
In simple words, serial dilution is the process of stepwise dilution of a solution with an associated dilution factor. In biology, serial dilution is often associated with reducing the concentration of cells in a culture to simplify the operation.

Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
Serial Dilution Objectives
- The objective of the serial dilution method is to estimate the concentration (number of organisms, bacteria, viruses, or colonies) of an unknown sample by the enumeration of the number of colonies cultured from serial dilutions of the sample.
- In serial dilution, the density of cells is reduced in each step so that it is easier to calculate the concentration of the cells in the original solution by calculating the total dilution over the entire series.
- Serial dilutions are commonly performed to avoid having to pipette very small volumes (1-10 µl) to make a dilution of a solution.
- By diluting a sample in a controlled way, it is possible to obtain incubated culture plates with an easily countable number of colonies (around 30–100) and calculate the number of microbes present in the sample.
Serial Dilution Formula and Calculations
- Serial dilution involves the process of taking a sample and diluting it through a series of standard volumes of sterile diluent, which can either be distilled water or 0.9 % saline.
- Then, a small measured volume of each dilution is used to make a series of pour or spread plates.
- Depending on the estimated concentration of cells/organisms in a sample, the extent of dilution is determined. For e.g., if a water sample is taken from an extremely polluted environment, the dilution factor is increased. In contrast, for a less contaminated sample, a low dilution factor might be sufficient.
- Serial two-fold and ten-fold dilutions are commonly used to titer antibodies or prepare diluted analytes in the laboratory.
- The dilution factor in a serial dilution can be determined either for an individual test tube or can be calculated as a total dilution factor in the entire series.
- The dilution factor of each tube in a set:

For a ten-fold dilution, 1 ml of sample is added to 9 ml of diluent. In this case, the dilution factor for that test tube will be:

- After the first tube, each tube is the dilution of the previous dilution tube.
Now, for the total dilution factor,
- Total dilution factor for the second tube = dilution of first tube × dilution of the second tube.
Example:
For the first tube, dilution factor = 10-1 (1 ml added to 9 ml)
For the second tube, dilution factor = 10-1 (1ml added to 9 ml)
Total dilution factor = previous dilution × dilution of next tube
= total dilution of 10-1 × 10-1 = 10-2
Online Serial dilution calculator
AAT Bioquest, Inc. (https://www.aatbio.com/tools/serial-dilution)
Omni Calculator (https://www.omnicalculator.com/chemistry/serial-dilution)
Endmemo (http://www.endmemo.com/bio/dilution.php)
Handymath (https://handymath.com/cgi-bin/serdil6.cgi?submit=Entry)
Tocris Bioscience (https://www.tocris.com/resources/dilution-calculator)
Physiology Web (https://www.physiologyweb.com/calculators/dilution_calculator_mass_per_volume.html)
Selleck Chemicals (https://www.selleckchem.com/dilutioncalculator.jsp)
ApexBio Technology (http://www.apexbt.com/dilution-calculator)
CiteAb (https://www.citeab.com/toolbox/dilutions)
Fluffy Frog (http://fluffyfrog.net/calc/)
Functional Biosciences (https://functionalbio.com/web/calc.php)
CUSABIO (https://www.cusabio.com/m-298.html)
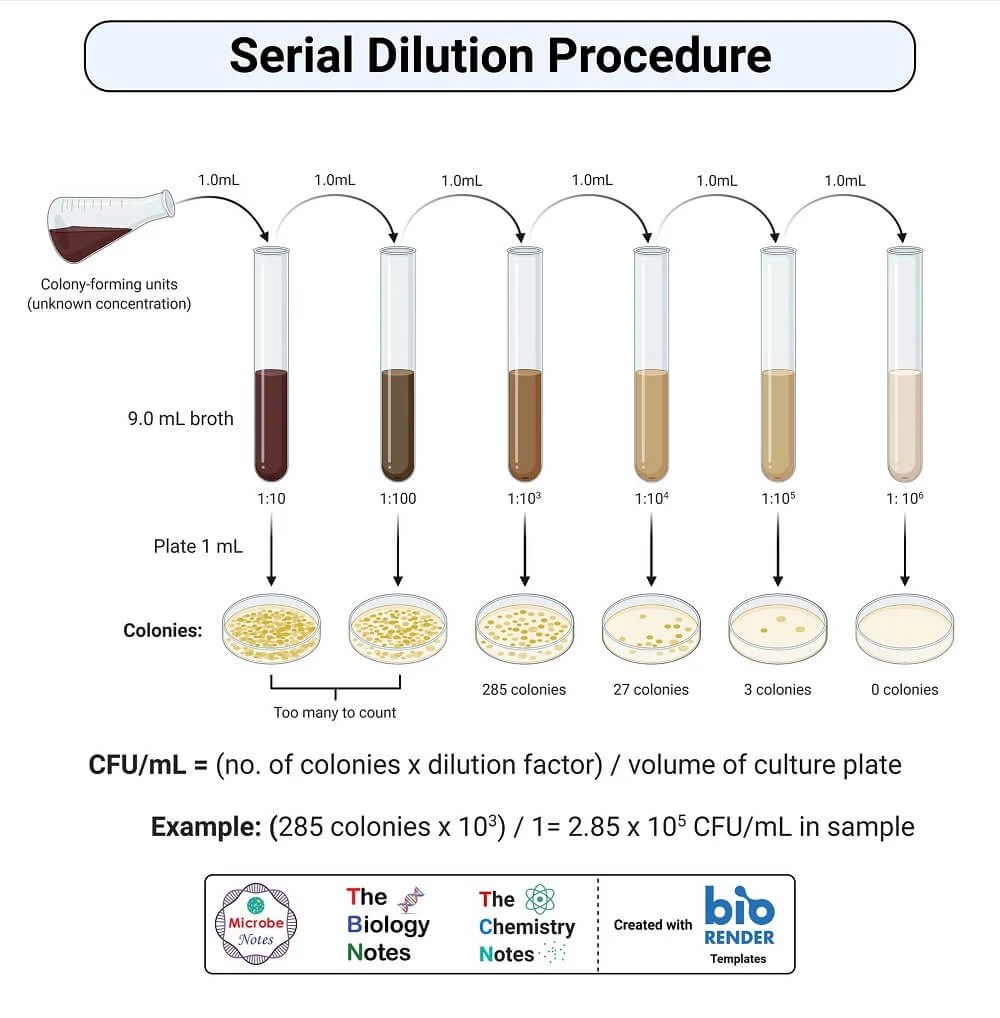
Procedure of Serial Dilution
The following is the procedure for a ten-fold dilution of a sample to a dilution factor of 10-6:
- The sample/culture is taken in a test tube and six test tubes, each with 9 ml of sterile diluents, which can either be distilled water or 0.9% saline, are taken.
- A sterile pipette is taken.
- 1 ml of properly mixed sample/culture is drawn into the pipette.
- The sample is then added to the first tube to make the total volume of 10 ml. This provides an initial dilution of 10-1.
- The dilution is thoroughly mixed by emptying and filling the pipette several times.
- The pipette tip is discarded, and a new pipette tip is attached to the pipette.
- Now, 1 ml of mixture is taken from the 10-1 dilution and is emptied into the second tube. The second tube now has a total dilution factor of 10-2.
- The same process is then repeated for the remaining tube, taking 1 ml from the previous tube and adding it to the next 9 ml diluents.
- As six tubes are used, the final dilution for the bacteria/cells will be 10-6 (1 in 1,000,000).
Applications of Serial Dilution
Serial dilution is performed in a number of experimental sciences like biochemistry, pharmacology, physics, and homeopathy.
- Serial dilution is used in microbiology to estimate the concentration or number of cells/organisms in a sample to obtain an incubated plate with an easily countable number of colonies.
- In biochemistry, serial dilution is used to obtain the desired concentration of reagents and chemicals from a higher concentration.
- In pharmaceutical laboratories, serial dilution is performed to receive the necessary concentration of chemicals and compounds, as this method is more effective than individual dilutions.
- In homeopathy, homeopathic dilutions are used where a substance is diluted in distilled water or alcohol. It is believed that dilution increases the potency of the diluted substance by activating its vital energy.
Limitations of Serial Dilution
Even though serial dilution is a useful technique in laboratories, it faces some challenges. Some of which are:
- An error might occur during the propagation of the sample, and the transfer inaccuracies lead to less accurate and less precise transfer. This results in the highest dilution to have the most inaccuracies and the least accuracy.
- Because serial dilution is performed in a stepwise manner, it requires a more extended period of time which limits the efficiency of the method.
- Serial dilution only allows the reduction of bacteria/cells but not the separation of bacteria/cells like in other techniques like flow cytometry.
- This technique also requires highly trained microbiologists and experts in aseptic techniques.
Serial Dilution Examples
- A simple example of serial dilution performed in our daily life is tea or coffee. In coffee, we add a certain amount of cold press coffee and add water over it to obtain a desired concentration of coffee.
- Another example of serial dilution is the dilution of acids and bases in chemistry to obtain a required concentration.
- Serial dilution of culture to determine the number of bacteria in a given sample through a plating technique is also an essential example of serial dilution.
References
- Basic Practical Microbiology-Manual. The society of General Microbiology. Retrieved from https://microbiologyonline.org/file/7926d7789d8a2f7b2075109f68c3175e.pdf
- Avishai Ben-David, Charles E. Davidson, Estimation method for serial dilution experiments, Journal of Microbiological Methods, Volume 107, 2014, Pages 214-221, ISSN 0167-7012,
- Cullen, J. J., & MacIntyre, H. L. (2016). On the use of the serial dilution culture method to enumerate viable phytoplankton in natural communities of plankton subjected to ballast water treatment.Journal of applied phycology,28(1), 279–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0601-x
- https://www.biomol.com/dateien/Bethyl–Serial-Dilutions.pdf
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Ancillary_Materials/Laboratory_Experiments/Microbiology_Labs/Microbiology_Labs_I/04%3A_Dilution_Worksheet_and_Problems