The network switch is a crucial component of any network—thus, understanding its role is paramount. This article aims to define what Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches are, discuss their differences, and help you decide which type is best suited for your business network.
To begin with, let’s define what a network switch is.
Network Switches Defined
TechTarget describes the network switch as follows:
“A network switch connects devices (such as computers, printers, wireless access points) in a network to each other and allows them to ‘talk’ by exchanging data packets. Switches can be hardware devices that manage physical networks, as well as software-based virtual devices.
Switches form the vast majority of network devices in modern data networks. They provide the wired connections to desktop computers, wireless access points, industrial machinery, and some internet of things (IoT) devices such as card entry systems. They connect the computers that host virtual machines (VMs) in data centers, as well as the physical servers and much of the storage infrastructure. They carry vast amounts of traffic in telecommunications provider networks.”
The terms “Layer 2” and “Layer 3” come from the OSI Model.
What is the OSI model?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model was created in 1984 and is a conceptual framework used to help visualize how a network functions. Although today’s modern internet is based on the simpler TCP/IP model, the OSI model is still used today to describe network architecture—and is split into seven different abstraction layers:
- Physical Layer (Layer 1)
- Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
- Network Layer (Layer 3)
- Transport Layer (Layer 4)
- Session Layer (Layer 5)
- Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
- Application Layer (Layer 7)

What is Layer 2 switching?
Layer 2 switching works on the Data Link Layer and uses network-device, Media Access Control (MAC) Addresses to determine where to forward frames. Both switches and bridges are used in Layer 2 switching to break up a large collision domain into multiple smaller ones.
As its name implies, a collision domain is an area of the network where data packet collisions occur. For example, a collision can happen when two network devices on a shared segment send a data packet simultaneously. If the packets collide, both devices must re-send their packets, reducing network efficiency.
All devices in a LAN are typically connected to one central device. Back in the day, the central device was usually a hub. However, hubs have distinct drawbacks, such as being oblivious to the traffic passing through them and creating one large collision domain. Bridges were designed to break up large collision domains to overcome these problems. Even so, bridges are not a perfect solution as they have a limited number of ports. Switches are widely used today as they have more ports than bridges, inspect incoming traffic, and make forwarding decisions. As each port on a switch is a separate collision domain, no collisions will occur.

What are the functions of Layer 2 switching?
In short, here is what a Layer 2 switch does:
- Learn the MAC address of the device on the switch port that receives the frame.
- Does two types of message forwarding: 1) Unicast and 2) Unknown Unicast (also called flooding). Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) is used.
- Forwards a frame through only the switch port that it has already learned the MAC address (called filtering)
- Uses Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to avoid looping
- Executes the same function as a transparent bridge
- Splits a complicated LAN into small Virtual Local Area Network (VLANs).
What are the benefits of Layer 2 switching?
There are plenty of reasons to use a Layer 2 switch in a LAN. Here are the major advantages:
- Faster than routers
- Hardware-based bridging
- Low cost
- Low latency
- Wire-speed
What is Layer 3 switching?
The main difference between a Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch is the routing function. A Layer 3 switch (also called a multilayer switch) performs all the functions a Layer 2 switch does; however, it has both static and dynamic routing functions. In other words, Layer 3 switching combines the functionality of both a switch and a router by inspecting incoming packets and making routing decisions that are based on source and destination addresses.

What are the functions of Layer 3 switches?
The layer 3 switch works on both OSI Data Link and Network layers. It has all the functionality of Layer 2 switches discussed above and, in addition, has routing capabilities. Layer 3 functionality can take either of two forms:
- Cut-through switches: With this switching method, only the first of a series of packets is looked at to determine the destination IP address. The remaining packets in the series are shifted to the MAC address. As a result, data throughput rates are higher.
- Packet-by-Packet Layer 3 (PPL3) switches: With this method, each packet in a series is looked into individually to determine its IP address. The PPL3 switch has a routing function built into its hardware and functions as a high-speed router. In addition, PPL3 switches perform other standard router functions such as:
- Verifying a packet’s integrity by using its checksum
- Updating a packet’s Time to Live (TTL) after each hop
- Processing all optional information in a packet’s header
What are the benefits of a Layer 3 switch?
Here are the major benefits of a Layer 3 switch:
- Supports routing between VLANs
- Improves fault isolation
- Simplifies security management
- Reduces broadcast traffic volume
- Eases the configuration process as a separate router is not needed between VLANs
- Improves traffic segregation with the use of routing tables
- Simplifies troubleshooting
- Lowers network latency

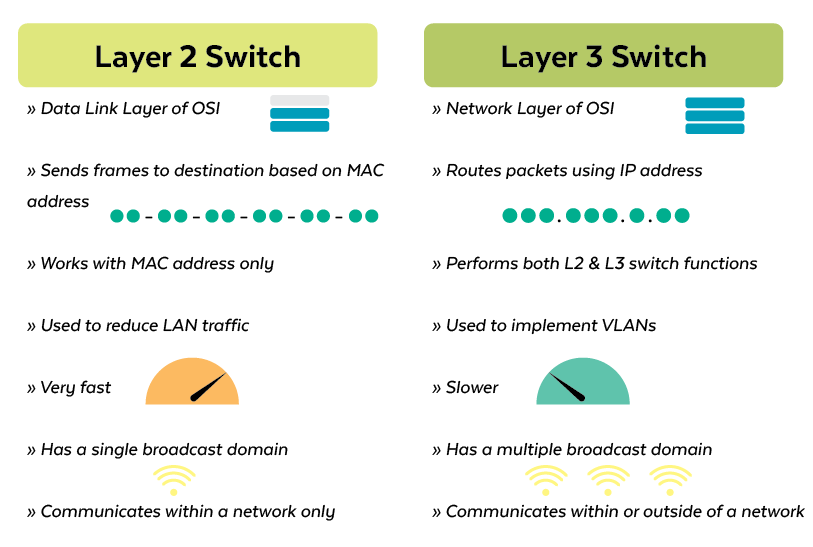
What are the differences between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches?
Following is a comparison of the key differences between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches:
Summary
Which type of switch you choose depends upon your needs. Layer 2 switches are often used to reduce data traffic on a LAN. Because they use MAC addresses only, an unidentified device attempting to use the network will be denied.
On the other hand, Layer 3 switches are primarily used to operate VLANs and improve security. VLANs help reduce collisions and create better data flow. Layer 3 switches help congested networks to speed up data rates.
Bottom Line: If you need a simple switch for fast, in-network communication, the Layer 2 switch is the solution. However, if you need a switch that can directly connect to devices outside your network without using a router, then a Layer 3 switch is the answer.
Planet Technology USA has an extensive supply of Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches from which to choose. Check out our Layer 2, 24-port switch or our Layer 3, 24-port switch. We are happy to help you!.